Primer on a 1031 Exchanges
1031 Exchanges…
It’s a Deferral
A mechanism to defer your capital gains taxes through real estate
What are Capital Gains?
Capital gains is the profit (gain) from the sale of any asset. Businesses, investment real estate, vehicles, etc.
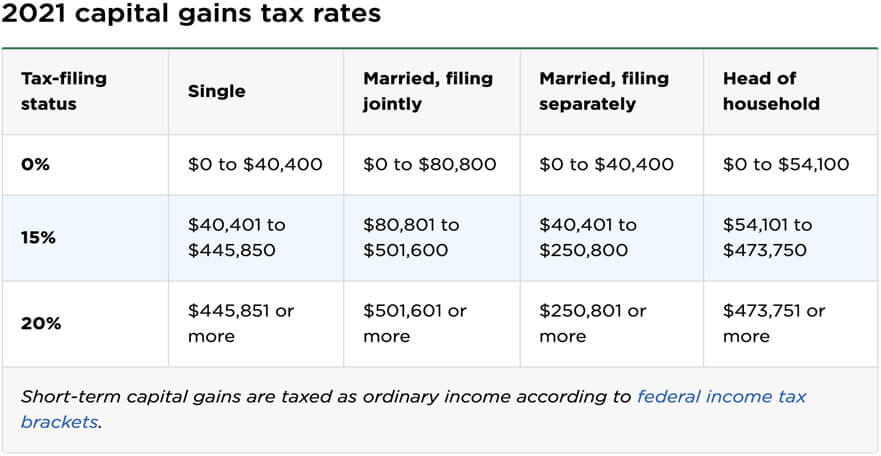
LONG TERM GAINS: for assets held longer than 12 months, your tax rate is 15% for under $445,000 in gains, or 20% if more.
SHORT TERM CAPITAL GAINS: For investments held shorter than 12 months, are treated as ordinary income and you are taxed at your individual or corporate income tax rate.
What are Capital Gains? Example
Purchase & Sale
You purchased a real estate investment property and sold it for a profit 13 months after you purchase date.
Your purchase price is $350,000
You invest $100,000 to rehab the property.
You sell the property 13 months later for $650,000.
Cost of Investment
Total Cost of Investment:
$350,000 PP
$100,000 Rehab
+$50,000 CC, comm, etc
Total Cost = $500,000
Capital Gains Tax
$650,000
- $500,000
Capital Gains = $150,000
$150,000 x 15% =
$22,500 in IRS taxes
What is a 1031 Exchange?
Internal Revenue Code Section 1031 (IRC Section 1031) is part of the tax code that allows you to postpone your capital gains tax payment if you reinvest the proceeds in a similar property as part of a qualifying like kind exchange.
- Postpone?
- Proceeds?
- Reinvest?
- Qualifying?
- Like Kind?
Internal Revenue Code Section 1031 (IRC Section 1031) allows you to postpone your capital gains tax payment if you reinvest the proceeds in a similar property as part of a qualifying like kind exchange.
Postpone - delay the payment of the taxes you have to pay as a result of the capital gains generated from the sale.
Proceeds - net proceeds from the asset sale after all closing costs and expenses.
Reinvest - use proceeds from a sale, to purchase another more expensive asset
Qualifying - the new asset and the purchase structure for the reinvestment meets the strict standards of the IRC 1031
Like Kind - the reinvested asset must be of the same nature, character, or class.
What is a Qualifying Like-Kind Exchange?
Qualifying Like Kind - the new asset and the purchase structure for the reinvestment meets the strict standards of the IRC 1031 and the reinvested asset must be of the same nature, character, or class.
1. Both the sold property and reinvestment property must be held for use in a trade or business or for investment purposes.
Examples:
Qualified: sold a 1-4 unit residential investment property, then you purchase a 1-4 unit residential investment property.
FAIL: Sold a commercial warehouse and purchased a Semi tractor Trailer
FAIL: Sold a Commercial industrial facility purchased a 20-unit Residential Building
Qualified: Sold a 20 Unit Residential Building, Purchased a 60-unit mixed use building.
FAIL: Personal residences or Second homes/Vacation homes
Qualifying Like Kind - the new asset and the purchase structure for the reinvestment meets the strict standards of the IRC 1031 and the reinvested asset must be of the same nature, character, or class.
2. Personal Property CAN be exchanged for personal property, and Real Property for Real Property.
3. CANNOT exchange Personal for Real.
4. The following assets are excluded from Section 1031:
- Inventory
- Stock in trade Stocks, bonds, or notes,
- Other securities or debt
- Partnership interests
- Certificates of trust
When do I do a Qualifying Like-Kind Exchange?
SIMPLEST 1031 EXCHANGE is a simultaneous swap of one property for another
1) You exchange your property and switch titles on the property with Seller
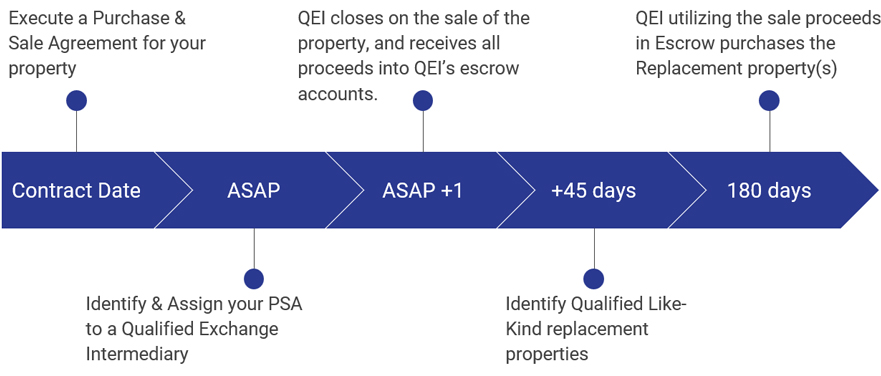
What is a Deferred 1031 Exchange?
A Deferred 1031 Exchange is more complex yet a more flexible transaction.
- Gives the Seller more time to identify and close on replacement options.
- Your property Sale and Purchase of the Replacement happen at different times.
- Proceeds from sale directly towards the purchase of the replacement property (ies),
- Deferred Exchange is essentially one prolonged mutually dependent transaction based on an exchange of property.
- You cannot take control or possession of ANY cash proceeds.
- If you take control of any proceeds you will disqualify the 1031.
Successful 1031 exchanges use a QUALIFIED EXCHANGE INTERMEDIARY.
Implementing a 1031 Exchange
What is a Deferred 1031 Exchange?
QUALIFIED EXCHANGE INTERMEDIARY (QEI):
This is an independent 3rd party that facilitates the entire 1031 exchange, a sophisticated and complex escrow agent.
QEI must take full control of the entire transaction and take the Seller out of the transaction, and the Seller becomes a distant observer to the transaction.
TWO TIME LIMITS ON A DEFERRED EXCHANGE
- 45 days from date you sell the relinquished property
- You have 45 days to identify a number of potential replacement properties.
- In writing to a person involved in the exchange
- Seller of Replacement Property or the Qualified Exchange Intermediary
- Real Estate Broker, attorney, or accountant DOES NOT COUNT
- Replacement property must be clearly identified
- Address, Pin, Legal description, or name
- In writing to a person involved in the exchange
- You have 45 days to identify a number of potential replacement properties.
- 180 Days to Purchase Replacement Property
- You must close and receive the Replacement property within 180 days of the original Sale, or
- Prior to Income tax return filing due date (with extensions) that sale of the property took place
- Whichever is earlier.
How Many Qualifying Like-Kind Exchange?
There are 3 possible ways to identify Replacement Properties
- Straight number = Pick 3 potential replacement purchases for more than Proceeds
- 200% rule = You can identify more than 3 properties if the combined value of the identified properties does not exceed 200% of the sold property’s value
- 95% rule exchanger may identify unlimited # of properties regardless of sale price of the relinquished property, BUT must acquire and close on 95% of the values identified.
- if you acquire less than 95% then the entire exchange will be considered invalid.
Impact
Defer your taxes for years until the final sale of your assets
Benefits of 1031 Exchange
There are 3 possible ways to identify Replacement Properties
- Continuous deferral of your tax liability for decades if you can keep it up.
- You can sell, replace, sell, replace, sell, replace for years and each time your capital gains may be increasing however you don’t pay taxes until that final sale without a replacement.
Sell: $500,000,
Purchase: $600,000,
Sell: $800,000,
Purchase: $1,000,000
Sell: $1,625,000
Capital gains tax on a once on the final $625,000 in Capital Gains

